Diabetes can be an issue for anyone, however, type 2 is more prevalent in middle-aged and elderly people. It is caused when the body is unable to produce enough effective insulin. Insulin is what allows glucose in the bloodstream to enter the cells. If there isn’t enough insulin produced then blood sugar will become too high which can cause a number of problems. There are a number of symptoms of diabetes in the elderly, and it is important to recognise them, otherwise they may be missed and lead to complications. Even if you or a loved one has been diagnosed already as someone gets older it can become more difficult and complicated to manage diabetes. Residential care can be a valuable option in this case.
What is the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes?
There are many types of diabetes, however, the most common types are type 1 and type 2.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes accounts for 8% of diabetes diagnoses. It is caused when the body can’t produce enough insulin, or the insulin it produces isn’t effective. This means the glucose from food stays in the bloodstream which can cause dangerous spikes in blood sugar.
In type 1 diabetes insulin production is minimised as the body attacks the cells in the pancreas which produce insulin.
It is unknown what causes type 1 diabetes to develop and it is often diagnosed in younger people.
What is Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a lot more common (90% of diabetes cases.) Type 2 diabetes is caused by lifestyle factors and will often become apparent later in life.
Type 2 diabetes is caused when the body builds up a resistance to the insulin produced which is needed to allow the cells to use blood glucose as energy. When resistance is developed the pancreas will produce more and more insulin but is unable to keep up with demand as much more insulin would be needed to allow the body to operate at a normal level.
Type 2 diabetes has a number of known causes, such as:
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Unhealthy diet
- Ethnicity
- Obesity
- Family history of diabetes
Why is Insulin Important
Insulin is essential to the body. It is a hormone produced in the pancreas that keeps blood sugar (glucose) stable. Insulin is important for turning the food we eat into energy for the cells.
When we eat it is broken down into blood sugar. The spike in blood sugar alerts the pancreas to release insulin and the insulin allows blood sugar to enter the cells. It also tells the liver to store blood sugar for if it is needed later. Once the blood sugar has decreased (used by the cells and stored in the liver) insulin levels decrease. If the insulin levels go too low from a lack of blood sugar then the liver is alerted to release what it has stored.
This process can become less effective if too much sugar enters the bloodstream, causing an increase in insulin production. Over a period of time cells can become less responsive to insulin and develop resistance. After that, the pancreas will keep trying to make insulin but will be unable to match the demand of the resistant cells which can lead to blood sugar continuing to rise, resulting in type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Symptoms in the Elderly
There are many warning signs to watch out for which can be symptoms of diabetes. In the elderly especially many can often go unnoticed and just be attributed to getting older. However, it is important to keep an eye out for changes in yourself and loved ones, and speak to a Doctor. if any of the following symptoms become apparent.
Tiredness
Due to the lack of insulin, or the development of insulin resistance, blood sugar cannot make it into the cells. This means the cells don’t receive the energy they need which can lead to feelings of tiredness. Tiredness is hard to attribute to one issue and can often be wrongly overlooked as a normal part of ageing. However, if you or a loved one starts to experience regular and uncharacteristically stronger feelings of tiredness then this could be a sign you should visit your doctor.
Increased Hunger
When the cells aren’t getting enough glucose to operate correctly signals will be sent to the brain to stimulate hunger. If you or a loved one is uncharacteristically hungry and if still feeling the urge to eat after a meal then this could be a symptom of type 2 diabetes.
Frequent Urination & Thirst
When blood sugar can’t make its way into the cells it stays in the blood, this puts a strain on the kidneys to filter excess glucose. If the kidneys struggle to keep up then glucose is excreted in the urine, and this takes extra liquid from the tissues of the body with it, leading to dehydration. This increases water intake, and therefore urination.
If you are concerned about frequent urination or thirst then it can be beneficial to keep a water intake journal, this can be especially helpful to show your Doctor if needed.

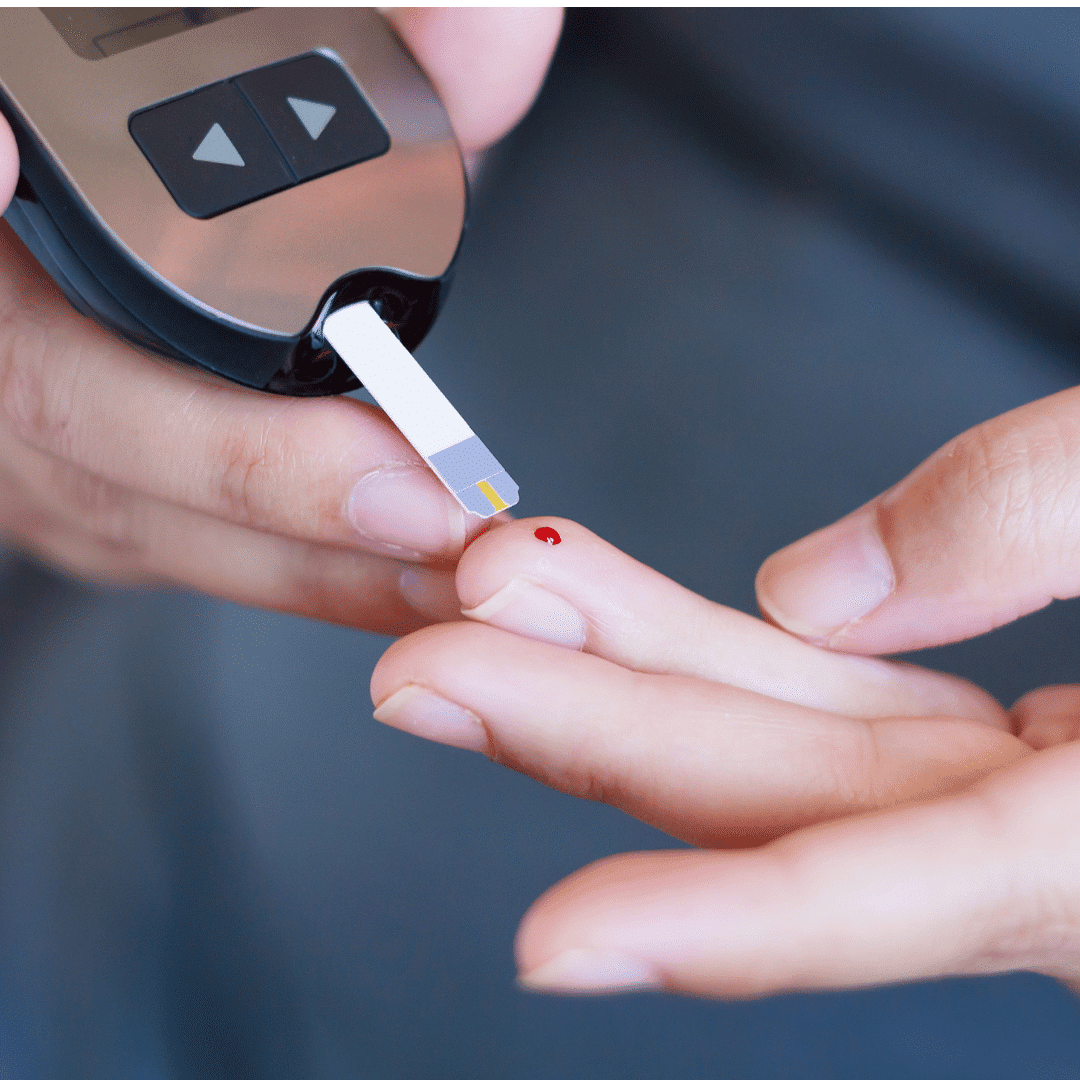
How do you get Diagnosed With Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is usually tested for in the blood or urine. Often, type 2 diabetes will be accidentally diagnosed from a blood or urine test for a different issue. However, if you or a loved one is experiencing any of the symptoms outlined above it is time to speak to your GP.
If you are experiencing the above symptoms then your GP can arrange a blood or urine test, which can often take 1 to 2 days to receive results.
How can the Elderly Manage Diabetes?
There are always changes that can be made to limit the effects of diabetes on the elderly, whether these are in the form of medicine, or lifestyle changes. Once diagnosed with diabetes your Doctor or GP will be able to advise on the best course of action.
Increased Physical Activity
An increase in activity can make the body more sensitive to insulin. When looking to increase your physical activity levels it is important to take it slow in order to not cause injury. If you are not used to regular exercise then jumping to go for a run every day may not be the answer. Instead, just increasing time spent walking can be hugely beneficial.

Changes to Diet
There are many diet modifications that can be made to help elderly people living with diabetes.
Increase Healthy Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are what the body breaks down into glucose, so it is important to monitor the types and amount of carbohydrates being consumed. You should be aiming to cut down on processed carbs like cereals and white bread, and instead increase the intake of whole grains, fruit, vegetables, and pulses.
Reduce Intake of Added Sugar
Reducing sugar intake can help to control glucose levels in the body. Though this can be difficult at first, simple swaps like sugar in hot drinks for sweeteners can help.
Reduce Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol by nature contains a large amount of sugar, which can make it harder to keep track of your glucose levels. Reducing alcohol intake is a quick way to reduce sugar intake.
Don’t Rely on “Diabetic Food”
Some food may be marketed as “diabetic food” with the promise of managing blood sugar levels, however, it is now against the law to make these claims. There is no scientific evidence to back up that these foods are any better than sticking to a healthy diet.
Insulin Shots
Insulin shots, or insulin pens, can be a helpful way to keep insulin levels optimal throughout the day. They are simple, discreet and can be prescribed by your Doctor. There are also smart insulin pens which are available through the NHS which can send information to an app to help keep track of insulin doses.
Pills
There are a multitude of medications available for treating the symptoms of diabetes. Your Doctor may prescribe different types in order to find the best fit for you.
How Can Little Croft Care Home Help?
At Little Croft Care Home, our team is experienced in looking after residents with diabetes. Whether this is ensuring medication is taken on time or that blood sugar levels are checked regularly, we ensure the comfort of everyone in our care.
Food at Little Croft is also healthy and fresh, we take into account the likes and dislikes of our residents, as well as their medical needs.
If you have a loved one who could do with a little extra help with managing their diabetes then we can help, while allowing them to maintain independence and dignity. If you would like to find out more, or just have a chat about options then get in touch today.

